Unlocking the Secrets: Exploring the World of Captive Insurance
Welcome to a captivating journey into the realm of captive insurance, a unique and fascinating concept in the world of risk management. Captive insurance, also known as microcaptive insurance, is a specialized form of self-insurance that allows companies to create their own insurance company to cover their specific risks. This alternative strategy offers numerous benefits, from potential cost savings to increased control over insurance coverage.
One fundamental aspect of captive insurance is the IRS 831(b) tax code, which provides specific tax advantages for small captives. By qualifying under this code, companies can enjoy significant tax benefits such as tax-exempt underwriting profits. Emitting a sense of empowerment, this tax code has driven the popularity of captive insurance and attracted businesses from various industries seeking to safeguard their interests.
Join us as we delve deep into the intricacies of captive insurance and peel back the layers of its inner workings. From examining the core principles to exploring real-life examples, we will uncover the comprehensive framework that companies utilize to unlock the full potential of captive insurance. Are you ready to embark on this eye-opening exploration? Let us embark on an enlightening journey into the world of captive insurance.
Understanding Captive Insurance
Captive insurance is a unique form of risk management that allows businesses to create their own insurance company to cover their self-insured risks. This alternative insurance arrangement is becoming increasingly popular among small to medium-sized enterprises due to its potential benefits. One important aspect to consider when delving into the world of captive insurance is the IRS 831(b) tax code, which provides specific guidelines for qualifying captives.
Check It Out
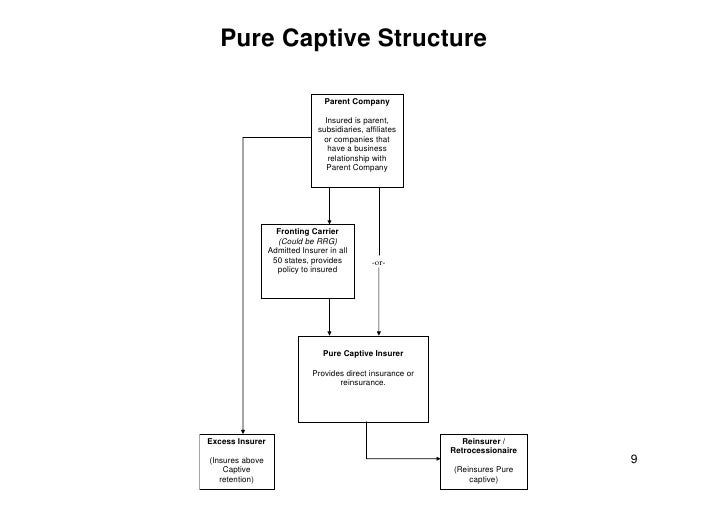
The concept of captive insurance involves an operating company forming its own insurance company, known as a captive insurer. The captive insurer then provides coverage for the risks faced by the operating company, which may include property damage, liability, or other specialized forms of coverage. By creating their own captive insurance company, businesses can gain greater control over their insurance programs and tailor coverage specifically to their needs.
An important term related to captive insurance is a microcaptive. A microcaptive is a small captive insurer that meets certain criteria outlined in the IRS 831(b) tax code. This code allows small captives to elect to be taxed only on their investment income, rather than their entire premium income. This attractive tax advantage has led to the rise in popularity of microcaptives as a cost-effective insurance solution for many businesses.
In summary, captive insurance provides businesses the opportunity to take control of their insurance programs by forming their own insurance company. The IRS 831(b) tax code and the concept of microcaptives play key roles in this alternative risk management strategy. This section serves as an introduction to the world of captive insurance, setting the stage for further exploration into its intricacies and potential benefits.
Exploring the IRS 831(b) Tax Code
The IRS 831(b) tax code is an important aspect when delving into the world of captive insurance. This particular provision allows small captive insurance companies to qualify for certain tax benefits. It is essentially a way for these companies to achieve tax efficiencies and retain more of their underwriting profits.
Under the IRS 831(b) tax code, captive insurance companies that meet the specified criteria can elect to be taxed only on their investment income. This means that their underwriting income, which is the premium collected from policyholders, is not subject to federal income tax. Instead, only the investment income generated from the premiums is taxed.
One of the key requirements for a captive insurance company to qualify for this tax provision is that their annual written premium must not exceed $2.3 million. This threshold ensures that only small captives, also referred to as microcaptives, can take advantage of the tax benefits offered by the IRS 831(b) tax code.
In addition to the premium limit, captives must also comply with other requirements such as risk distribution and risk shifting. These terms refer to the diversification of risks and the transfer of risks from policyholders to the captive insurer. Meeting these requirements ensures that the captives are operating as legitimate insurance entities.
Exploring the intricacies of the IRS 831(b) tax code provides insights into the specific tax advantages available to captive insurance companies. By understanding the provisions and requirements, businesses can determine whether captive insurance is a viable option for managing their risks while also enjoying potential tax benefits.
Benefits of Microcaptives
Microcaptives, also known as 831(b) captives, offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive option for many businesses. One of the main advantages is the potential for significant tax savings. Under the IRS 831(b) tax code, premiums received by a microcaptive insurer are generally tax-exempt, allowing businesses to retain a larger portion of their insurance premiums.
In addition to tax savings, microcaptives also provide businesses with greater control over their insurance programs. By establishing their own captive, companies can tailor their coverage to meet their specific needs, rather than relying solely on the commercial insurance market. This flexibility enables businesses to customize their risk management strategies and obtain insurance coverage that truly aligns with their unique risks.
Furthermore, microcaptives can offer improved risk management and claims control. By self-insuring a portion of their risks through a captive insurer, businesses can have more direct involvement in the claims process. This can lead to faster and more efficient claims handling, as well as the ability to implement proactive risk mitigation measures.
Overall, microcaptives provide a valuable tool for businesses to effectively manage their risks and insurance programs. The potential for tax savings, increased control over coverage, and improved risk management make microcaptives an appealing option for those seeking alternative insurance solutions.